Over View
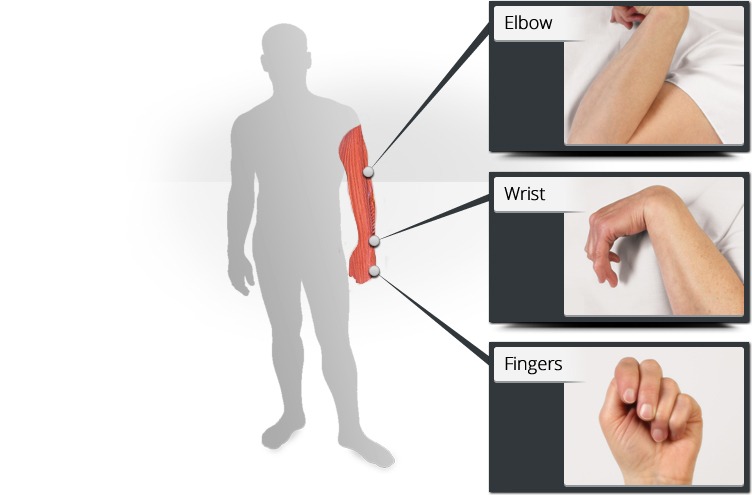
Spasticity is a condition in which muscles stiffen or tighten, preventing normal fluid movement. The muscles remain contracted and resist being stretched, thus affecting movement, speech and gait
Causes
Spasticity is generally caused by damage or disruption to the area of the brain and spinal cord that are responsible for controlling muscle and stretch reflexes. These disruptions can be due to an imbalance in the inhibitory and excitatory signals sent to the muscles, causing them to lock in place. Spasticity can be harmful to growing children as it can affect muscles and joints. People with brain injury, spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy or multiple sclerosis can have varying degrees of spasticity.
Symptoms
Symptoms of spasticity can vary from being mild stiffness or tightening of muscles to painful and uncontrollable spasms. Pain or tightness in joints is also common in spasticity.
- Muscle stiffness, causing movements to be less precise and making certain tasks difficult to perform
- Muscle spasms, causing uncontrollable and often painful muscle contractions Involuntary crossing of the legs
- Muscle and joint deformities
- Muscle fatigue
- Inhibition of longitudinal muscle growth
- Inhibition of protein synthesis in muscle cells
Testing & Diagnosis
Due to the varying degrees of spasticity, diagnosis may not be so simple. A physical examination with neurological testing will be done to test for spasticity and the severity of it. Imaging such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide more information on the source of spasticity and the extent of the damage that has caused it.
Treatment
Fortunately, there are several treatment options for spasticity and patients usually undergo more than one treatment at a time. The following treatments have been shown to effectively alleviate symptoms and improve quality of daily life.
Surgery
Intrathecal Baclofen (ITB) Pump: A pump can be surgically placed in a patient’s abdomen and will release a steady dose of baclofen directly to the spinal fluid. This allows for a significant reduction in spasticity and pain with fewer side effects compared to taking baclofen orally. ITB pump therapy should only be considered in extreme cases of spasticity and has been found to be most effective in treating spasticity in the lower and upper extremities. Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy (SDR): Spasticity can be caused by an imbalance in electrical signals to antagonist muscles. SDR rebalances the electrical signals sent to the spinal cord by cutting selective nerve roots. This is only done in severe spasticity of the legs. With proper and precise indication of the problematic nerve roots, cutting these roots will decrease muscle stiffness, while maintaining other functions. SDR is most commonly used in patients with cerebral palsy.